
The pillar of any building is its foundation, the component that transfers the weight of the structure onto the ground safely. It is an important factor in stability, durability and safety.
In a nation such as Nepal with its land characteristics of earthquake-prone areas, hilly land and the difference in soil conditions, a robust and well-strategised foundation is a necessity, rather than a choice. A well-constructed foundation is beneficial in resisting your home against cracks, irregular settling, and structural collapse during an earthquake.
Throughout this Blog, we will describe the various categories of house foundations used in Nepal and the reasons why it is necessary to have the right foundation to build a safe and durable foundation for your house.
The selection of the right kind of foundation depends on numerous factors, such as the place where your land is located. Engineers and homeowners should consider these before the construction.
Key factors include:
The knowledge of these factors helps builders to choose a safe, cost-effective and stable foundation to each site.
Foundations in Nepal are categorised into two types of foundation: Shallow Foundations and Deep Foundations, according to the depth and load-carrying capacity.
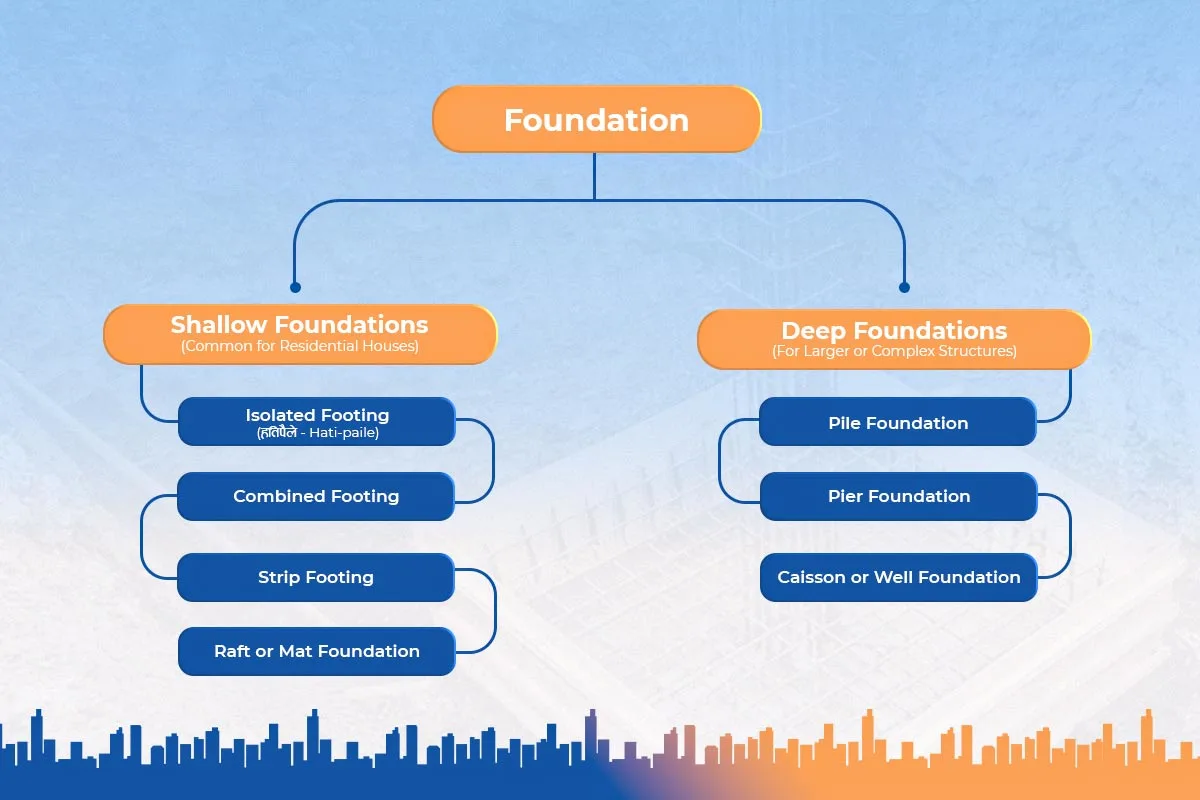
Shallow foundations are pilled near the ground surface, normally within a depth of 3 meters. They fit well in small and medium-sized houses and where the soil is stable.
Common types of shallow foundations in Nepal include:
It is a type of foundation that is very common in Nepali houses. The columns are standing on their own feet. It is simple, affordable, and applicable in homogenous soils. It is commonly used by engineers who want one or two-story houses built with RCC.
Combined footing is taken when the distance between two or more columns is narrow and their footing intersects. It also shares the load equally and avoids the occurrence of uneven settlements, particularly in urban plots where space is limited.
Load-bearing walls are supported by a strip footing rather than by supporting columns. It is self-supporting on the wall. It is typical of older city and countryside masonry houses in Nepal, which use brick and stone as their primary building materials.
A raft foundation distributes the weight of the building over a wide areas, and in most cases over the total building area. It is perfect for weak or uneven soil. Raft foundations are used in Kathmandu Valley, where clay soil is also prevalent, to inhibit cracks and settlement.
Deep foundations distribute the building load to deeper more strong soil layers or rock layers. They are intended in high-rise buildings, commercial constructions, and bridges.
Pile foundations consist of long, slim columns constructed using RCC or steel, and they go deep underground. They are highly supportive of high-rise structures or in places where the topsoil is loose. In Nepal, when the country has a higher risk of floods in the Terai Region, pile foundations are common in order to make the place stable.
Pier foundations are cylindrical columns which hold the structure on top of them. They can be mostly found in hillside areas houses, or where water has to pass under the structure, such as bridges or hillside houses.
This kind is constructed in soft soil or water. Caisson foundations are an effective type of foundation common in bridge and river construction projects in Nepal and are constructed with the use of large hollow cylinders sunk into the ground.
The foundation is not just a matter of choosing; the correct construction practice is the key to making it last long.
The following are some of the key tips to strong and safe foundations:
Every safe home relies on a solid foundation and Nepal is no exception, considering that there are earthquake-prone areas. The type of right foundation gives strength, stability, and decades of durability.
It does not matter where you are constructing a house in the hills or the plains, you have to rely on the specialists who know what Nepal soil and safety require. Want to get a safe and stable house? Get in touch with Jadan Construction Group.